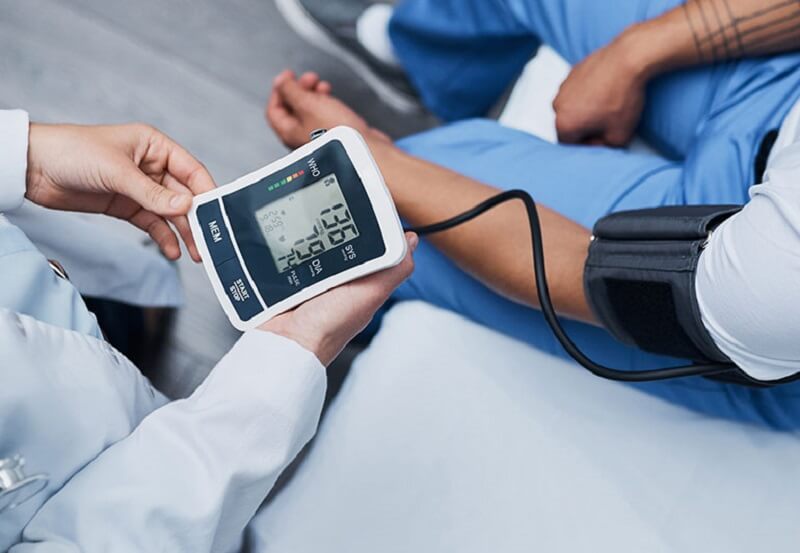
Blood pressure is the measure of the force exerted by the blood against the walls of the blood vessels.
The heart pumps blood to the blood vessels, carrying blood throughout the body.
High blood pressure, also called hypertension, is dangerous because it makes the heart work harder to pump blood to the body and contributes to the hardening of the arteries, or atherosclerosis, stroke, kidney disease, and heart failure.
RELATED: DASH Diet – For People With Hypertension
Why do you have high blood pressure? – Causes
The exact causes of hypertension can vary from person to person. However, it can be said that these are the leading causes of high blood pressure:
- Being overweight or obese
- Lack of physical activity
- Excessive consumption of salt and poor-quality fats
- Stress
- Smoke
- Drink alcohol (more than one drink per day)
- Diabetes
- Genetics – Family history of high blood pressure
- Chronic kidney disease
- Adrenal and thyroid disorders
- Sleep disorders
Symptoms of hypertension
Most people with hypertension have no symptoms, even when their blood pressure values reach dangerously high levels. This is why hypertension is also known as the “silent killer.”
Some people with high blood pressure may have headaches, ringing in the ears, shortness of breath, or nosebleeds, but these signs and symptoms are not specific. They usually don’t occur until high blood pressure has reached a severe or life-threatening stage.
Severe hypertension can cause fatigue, nausea, vomiting, confusion, anxiety, chest pain, and muscle tremors.
How do I know if I have high blood pressure?
It is good to have your blood pressure measured as part of your routine if you suffer from hypertension.
If you are 40 or older and at high risk for hypertension, ask your doctor for frequent readings at least 2-3 times per year.
If you don’t see your doctor regularly, you can find machines in some stores or pharmacies to measure your blood pressure quickly. While this way of measuring pressure is less accurate, it can help you understand your values.
The blood pressure values are:
- Normal: less than 120 over 80 (120/80)
- High: 120-129 / less than 80
- Stage 1 high blood pressure: 130-139 / 80-89
- Stage 2 High Blood Pressure: 140 and over / 90 and over
- Hypertension crisis: more than 180 / more than 120
RELATED: How to Lower Blood Pressure Without Medication?
Complications and consequences of hypertension
Excessive stress on the artery walls caused by high blood pressure can damage your blood vessels and your body’s organs. The higher your blood pressure and the longer it goes uncontrolled, the greater the damage.
Uncontrolled high blood pressure can lead to complications such as:
- Heart attack or stroke. High blood pressure can lead to hardening and thickening of the arteries (atherosclerosis), leading to a heart attack, stroke, or other complications.
- Aneurism. Increased blood pressure can cause blood vessels to weaken and bulge, forming an aneurysm. If the aneurysm ruptures, it can be life-threatening.
- It weakened blood vessels in your kidneys and liver. This can cause these organs not to work usually.
- Thickened, narrowed, or torn blood vessels in the eyes. This can result in vision loss or problems.
- Metabolic Disorder Syndromes – This is a group of disorders of your body’s metabolism, such as high triglycerides, bad cholesterol, and high insulin levels. These conditions make you more likely to develop diabetes and heart and brain disease.
- Problems with memory or understanding. Uncontrolled high blood pressure can also affect your ability to think, remember, and learn. Memory or understanding problems are more common in people with high blood pressure.
- Dementia . Narrow or blocked arteries can limit blood flow to the brain, which can cause a type of dementia called vascular dementia.
How to reduce hypertension?
Reducing high blood pressure prevents heart attacks, strokes, kidney damage, and other health problems. Here are some tips according to the WHO to prevent and reduce high blood pressure.
To prevent hypertension:
- Reduce salt intake (to less than 5 g per day)
- Eat more fruits and vegetables.
- Be physically active regularly
- To avoid the use of tobacco.
- Cut down on alcohol.
- Limit your intake of foods high in saturated fat.
- Eliminate/reduce trans fats in the diet
Also, doctors may recommend:
- Reduce and manage mental stress
- High blood pressure treatments
- Management of other medical conditions
ABSTRACT
Hypertension is a multifactorial disease; several causes can cause it.
Smoking, eating a lot of unhealthy fats, drinking alcohol, and being sedentary can cause your blood pressure to exceed average values.
Following healthy habits like eating right, exercising, and reducing stress can help lower high blood pressure.