Understanding how the immune system works is complex, even for scientists specialized in the subject.
The immune system is made up of many elements; whose operation depends on several factors.
However, some fundamental processes of the immune system are well known and can be simplified. This material will briefly review these mechanisms and how the immune system ensures its function – immunity.
RELATED: How to Strengthen the Immune System?
What is the immune system?
The immune system is all the molecules, cells, and mechanisms responsible for ensuring immunity.
The immune system includes all the strategies to defend against tissue damage and infection. And therefore, it is responsible for maintaining the integrity of the tissues.
The most classic example of these elements is white blood cells. However, the immune system is diverse and forms an interactive network that includes organs and proteins.
The word immunity comes from the word immunity, which refers to the protection against legal processes enjoyed by Roman senators. (1)
Today the term immunity refers to protection against disease, particularly against infectious diseases.
Although relatively recently, there has been a branch of science that studies this system – (immunology); Since the 1960s, our understanding of the immune system has been dramatically transformed.
What is the immune system for? – Function
The primary function of the immune system is a defense against infectious microorganisms – viruses and bacteria. However, the immune system can also trigger its response against other foreign substances.
Another essential function of the immune system is fighting against the body’s cells where dangerous changes are detected. This mechanism is necessary to ensure homeostasis and prevent tumor cells from developing.
The immune system works every day to fulfill its function. And, most of the time, we don’t even notice it. But when immunity fails is when we face a disease.
How does the immune system work?
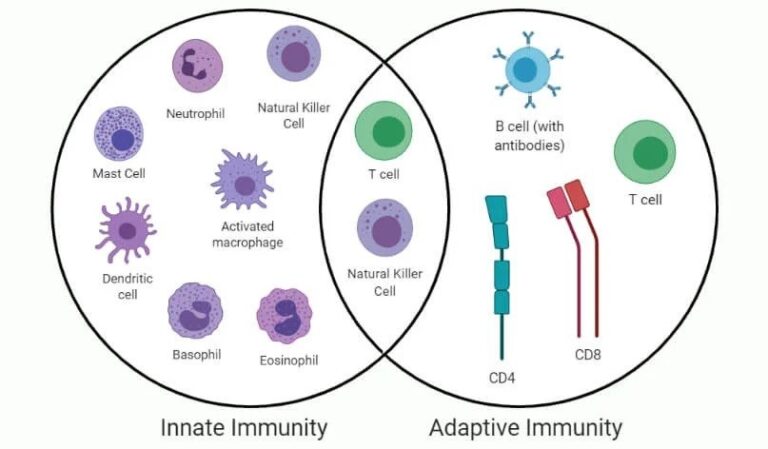
Defense against microbes is regulated by coordinated responses known as innate and adaptive immunity.
The innate immune system (natural or native) responds quickly to microbes and damaged cells. This response is the first line of defense, and it hardly changes over time.
The main components of innate immunity are:
- Physical and chemical barriers (skin, mucous membranes)
- Phagocytic cells (macrophages, neutrophils )
- Dendritic cells
- Mast cells
- NK lymphocytes
- Blood proteins (complement system)
Innate immunity fights microbes in 2 ways; recruiting cells that destroy pathogens and blocking the replication of viruses or infected cells.
On the other hand, there is adaptive immunity. This response is mediated by cells called lymphocytes and their products. Their defense mechanisms are more specialized and are found only in jawed vertebrates.
The main components of adaptive immunity are:
- T lymphocytes
- B lymphocytes
- Antibodies
Lymphocytes can recognize several signals as varied as the number in the body. This is up to a trillion possible threats to immunity.
The adaptive immune system response is exquisite and can generate memory. It increases when it detects the repeated attack of the same microbe.
These two systems – immune and adaptive – work in tandem. They communicate with each other to combat all possible dangers to our bodies.
What affects immunity?
The factors that affect immunity are various.
Our immunity is affected by an infection itself and by stress, hygiene, and the lack of nutrients in the diet. In addition, the quality and hours of sleep also play an essential role.
Genetics, age, use of medications and supplements can also affect immunity.
Factors that affect immunity are:
- Age
- Nutrition
- Hygiene
- Medications and supplements
- Levels of cortisol
ABSTRACT
The immune system is a complex system that includes organs, cells, and proteins.
The primary function of the immune system is to protect the body against infections (by viruses and bacteria). However, it can also fight against other threats and even kill defective cells of its own.
How does the immune system work? Protective immunity is controlled by early reactions – (innate immunity) and later responses (adaptive immunity). These two responses work in a coordinated and specific way to act in the face of each danger.
The mechanisms of the immune system are wide and varied; these range from neutralizing microbes so that they cannot infect, opening pores to break their membranes to generating antibodies to ensure defense in the future.