A drop in testosterone decreases libido, and erectile dysfunction is a typical complication of type 2 diabetes in men over 40. Studies show that up to 75% of people with diabetes face sexuality disorders 10 to 15 years earlier than those who are not.
Although obesity and low physical activity, usually the cause of diabetes, are serious risk factors for low male sex hormones. Taking Metformin, a blood-lowering drug also affects testosterone levels. However, not many people are aware of this side effect.
RELATED: Low Testosterone In Men – Causes and Symptoms
Diabetes and testosterone
Diabetes mellitus is a group of diseases associated with glucose and insulin metabolism disorders. Diabetes occurs when the body loses its ability to use the hormone insulin properly: it produces an insufficient amount or loses its sensitivity to its action.
In the case of type 2 diabetes, the most common, the body’s tissues lose their sensitivity to insulin. Although the hormone is present in the blood, it does not have the proper effect on glucose; as a result, blood sugar levels rise, leading to health risks (including vascular complications that affect erection).
Studies show that men with low testosterone levels have an increased risk of developing diabetes, obesity, and metabolic syndrome, factors that are collectively linked to sexual potency problems in men. (2)
Metformin to reduce sugar levels
Metformin is the most commonly prescribed drug for type 2 diabetes. It is one of the top five selling drugs; for example, in the United States, more than 80 million metformin prescriptions are written each year. (3)
Its reception inhibits the formation of glucose in the liver while reducing the percentage of its absorption (by changing the intestinal microflora) and increasing the sensitivity of tissues to insulin.
However, in addition to its primary function, Metformin reduces testosterone levels in men and women (for example, those with polycystic ovary syndrome).
Metformin lowers testosterone in people with diabetes
Testosterone is known to be the primary male sex hormone. Not only does it regulate potency and sexual behavior in men, it normalizes blood pressure, improves glucose utilization, and also maintains strength and muscle mass. Higher levels of testosterone help both prevent diabetes and better control it.
On the other hand, although it improves diabetes control and reduces the risk of its complications, a decrease in insulin resistance can negatively affect testosterone synthesis.
For this reason, traditionally, the consequences of diabetes (vascular and neurological complications) are considered a more dangerous for male sexual health than a decrease in testosterone levels.
Investigation
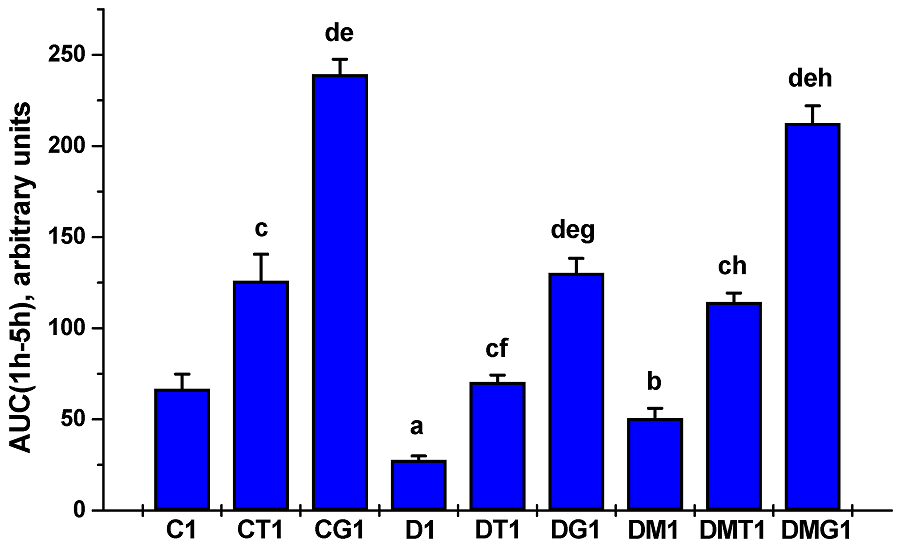
A systematic study compared the effect of Metformin and glibenclamide (a sulfonylurea drug) on testosterone (5). Recall that the principle of action of drugs: Metformin reduces the synthesis of glucose in the liver and insulin resistance, and glibenclamide stimulates the beta cells of the pancreas to produce more insulin.
Sixty-four patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus were divided into two groups: 34 people took Metformin, and 30 people took sulfonylureas (glibenclamide). The control group of healthy volunteers consisted of 27 people. The age of the participants ranged from 41 to 49 years.
The following metrics were compared for all participants: total testosterone and free testosterone, free androgen index (FAI), sex hormone transporting globulin (SHBG), cholesterol, and anthropometric parameters (height, weight, BMI, waist circumference, and percentage of body fat).
Results
Based on the data, the scientists conclude: “Metformin in type 2 diabetes leads to a significant decrease in testosterone levels, libido, and induction of erectile dysfunction caused by low testosterone levels, while sulfonylurea in the Type 2 diabetes leads to a substantial increase in testosterone levels, libido, and erectile function. “
Which is the reason?
Although Metformin’s effect on testosterone is not fully understood, scientists believe that metformin therapy lowers testosterone by inhibiting cytochrome P450-C17a, a key enzyme in the synthesis of steroid hormones.
ABSTRACT
When managing diabetes, men should consider not only diet, physical activity, and BMI but also the level of male sex hormones. Controlling glucose levels with medications such as Metformin can lead to low testosterone in men. If you experience symptoms of low testosterone, ask your doctor whether it is possible to replace Metformin with other therapies or medications.