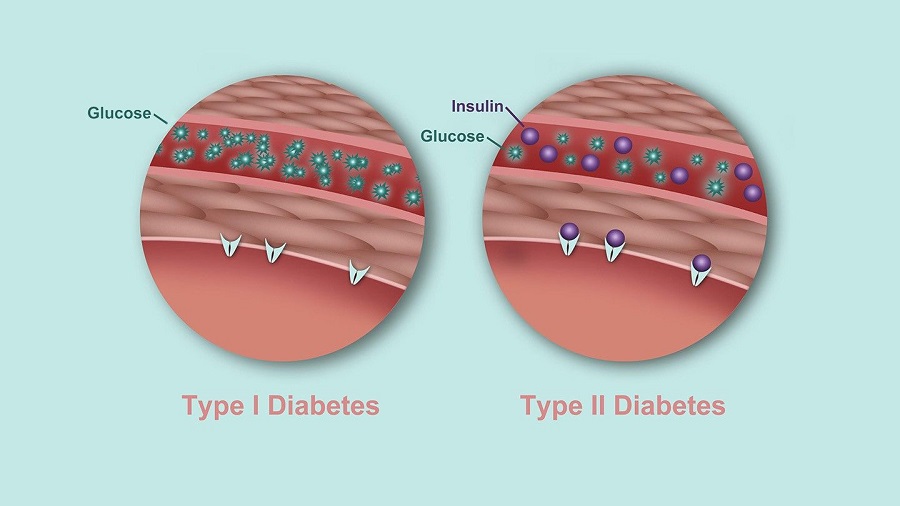
There are two main types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2. Both types of diabetes are chronic diseases that affect how your body regulates blood sugar or glucose.
Glucose is the fuel that fuels your body’s cells, but to enter your cells, you need a key; this is insulin.
People with type 1 diabetes do not produce insulin; it is as if you do not have that key.
People with type 2 diabetes do not respond to insulin as well as they should or do not make enough of it. You can think of this as having a broken key.
Both types of diabetes can cause complications, and the treatments are different. Read on to find out which ones they are and which one may be worse than another.
RELATED: Why Diabetes Can Lose Weight?
Differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes
Although both types of diabetes are associated with high blood sugar levels, their causes are different. In addition, the treatments tend to be different for each class.
Here is a table with the main differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
| Diabetes type 1 | Type 2 diabetes |
|---|---|
| The body cannot make insulin properly. | People are intolerant of insulin or do not make enough of it. |
| Cause: The immune system destroys insulin-producing cells. | Causes: genetics, diet, and sedentary lifestyle. |
| Uncommon a 5% of cases in the world. | Common 95% of cases in the world. |
| Symptoms generally begin in childhood or adolescence. People with type 1 diabetes need medical help for complications and illnesses caused by high blood sugar levels. | Symptoms may not appear before diagnosis. Symptoms generally appear in adulthood. |
| Low blood sugar episodes – hypoglycemia is common. | There are no episodes of low blood sugar unless they take insulin shots or medicine. |
| It cannot be prevented. | It can be prevented or delayed with a healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition. |
RELATED:
Which type of diabetes is worse, 1 or 2?
Answering which type of diabetes is worse is not an easy thing. Each case is unique, and both can cause complications.
People with type 1 diabetes need insulin to live, usually from a young age. But Type 2s can require vast amounts of insulin as your resistance increases.
Type 2s can live undiagnosed for several years and have complications when diagnosed. People with type 1 diabetes are usually diagnosed quickly and can act immediately.
But do types 1 with diabetes live for a more extended period? Not always.
Finally, let’s clear up a great myth. When someone has type 2 diabetes, it is not always their fault. Type 2 diabetes has a strong genetic link (even more than type 1). If your twin has type 2 diabetes, he has a nearly 100% chance of developing it.
While staying fit and eating right can delay and prevent the onset of type 2 diabetes, it doesn’t always guarantee prevention. You are likely to develop type 2 diabetes if you have the genes. What if you don’t have the genes? You can increase your risk factor.
RELATED:
How are type 1 and type 2 diabetes treated?
There is no cure for type 1 diabetes. People with type 1 diabetes do not produce insulin, so they must take regular injections. Testing your blood sugar is essential for managing type 1 diabetes because levels can rise and fall rapidly.
Although many people need additional support, type 2 diabetes can be controlled and even reversed with diet and exercise alone. If lifestyle changes aren’t enough, your doctor may prescribe medications that help your body use insulin more effectively.
In the case of type 2 diabetes, controlling blood sugar levels is the best way to know if you are reaching your goal. If your blood sugar levels are high, your doctor may recommend insulin injections.
RELATED:
ABSTRACT
Diabetes is a chronic disease in which sugar levels build up in the bloodstream.
In type 1 diabetes, your body cannot make insulin. In type 2 diabetes, the cells in your body cannot respond to insulin as well as they should.
With careful monitoring, you can normalize your blood sugar levels and prevent the development of severe complications in both types.