The insulin index or insulin index is an indicator that measures the amount of insulin that is generated in the body in response to the consumption of certain types of food.
This indicator is closely associated with the glycemic index , and the glycemic load . The fundamental difference is that an increase in insulin levels in the blood can be caused not only by the consumption of carbohydrates, but also by some foods high in protein.
The introduction of the insulin index is a merit of a group of researchers from the University of Sydney Holt SH and Jenny Brand-Miller were the innovators in this theory. It was thanks to his research on carbohydrate absorption mechanisms that the theory of the glycemic index and the insulin index (1,3) was born.
This article defines the concept of the insulin index and provides a table with examples of values in foods.
Related: Insulin – How does it work and what is its importance?
What is the insulin index or insulin index?
The insulin index is the most accurate indicator for measuring insulin response to food. In fact it is more accurate than the IG. This is because some foods such as lean meats and certain types of carbohydrates create a response in the body that was not taken into account.
The insulin index not only measures the ability to increase the level of glucose in the blood but the actual insulin response that occurs in the body when eating certain types of foods. The glycemic index does not take into account the combination of certain food groups.
A good example is the case that occurs with white rice, although the glycemic index is of the order of 110 units; the insulin index is about 80.
In contrast, the insulin index of yogurt is about 62 units and the insulin index about 110. For a person who must monitor insulin levels in the body, or must constantly measure blood glucose levels , this is essential.
What is the insulin index for?
The insulin index is used to theoretically determine the level of insulin in the blood after eating.
These data are useful for diabetics or prediabetics, as well as for those who have decided to lose weight through a low-carbohydrate diet .
The most important practical information is with products that contain lactose and are high in protein: milk, yogurts, ice cream. These cause a sudden release of insulin into the blood, although theoretically they do not have a high GI.
While it is theorized that avoiding foods high in sugar is essential to prevent insulin resistance , it is also recommended to avoid combinations of dairy with sweets as much as possible.
Differences between insulin and glycemic index
The glycemic index theory does not consider the effect on insulin levels in foods that do not have carbohydrates; it is understood that they do not affect blood sugar levels and have a GI equal to 0.
However, research has confirmed that combining carbohydrates with meats does increase insulin levels; which has led to recalculate this theory. (3,4)
The reason: combining certain amino acids (histidine, methionine, and valine) with carbohydrates creates a synergistic effect that raises insulin levels.
While carbohydrates are key in generating a response to insulin; they are not solely responsible. Amino acids alone are not capable of modifying these levels (in fact it is the basis of low carbohydrate diets such as the ketogenic diet ). However, it is true that high-carbohydrate-protein foods stimulate this response.
How to use the insulin index?
A diet based on the glycemic index emphasizes avoiding certain food groups, particularly those that are high in simple carbohydrates and refined flours.
It implies an almost complete exclusion of sweet foods, bakery products, wheat flour, white rice, potatoes.
The glycemic index does not take into account the effect of meats, nor does it consider the effect of protein foods.
The insulin index theory makes some adjustments. First, the effect of the insulin level on protein products, mainly lean meats and fish, is considered.
Second, the data on the effects of carbohydrate-protein combining foods are adjusted. Although they may have a moderate GI, their consumption leads to a significantly higher release of insulin in the blood (2). This mainly occurs in foods that contain lactose in their composition.
Insulin index – food tables
Determining the insulin index of foods was not an easy task. For this, the amount of insulin that a food generates after ingesting it on an empty stomach was calculated with experiments.
The authors of the theory point out that in a real situation the values presented in tables, although they may differ, (depending on the physical state of a person) are more precise in the effects they generate in response to insulin.
To determine the GI, a serving of approximately 50 g of pure carbohydrates was measured. Whereas to calculate the insulin index of food it is calculated for a portion of 1000 kilojoules (or approximately 240 kcal) ².
Below is a table with the insulin index of foods:
| Food | IG | Insulin index |
| Candies | 100 | 120 |
| Sweet chocolate tablet | 79 | 120 |
| Potato | 70 | 115 |
| Yogurt | 62 | 115 |
| White bread | 100 | 100 |
| Pan integral | 75 | 80 |
| Cookies | 80 | 92 |
| Ice cream | 70 | 89 |
| Sweet cakes | 70 | 85 |
| Grapes | 70 | 82 |
| White rice | 90 | 79 |
| Cornflakes | 76 | 75 |
| Potato chips | 71 | 75 |
| Integral rice | 70 | 60 |
| Oranges | 40 | 60 |
| Fish | 28 | 60 |
| Apples | 50 | 59 |
| Lentils | 62 | 58 |
| Popcorn | 62 | 59 |
| Red meat | 25 | 55 |
| Sugar free muesli | 40 | 55 |
| Cheeses | 55 | 50 |
| Carrots | 40 | 50 |
| Eggs | 40 | 30 |
| Peanuts | 12 | 20 |
What is the function of insulin?
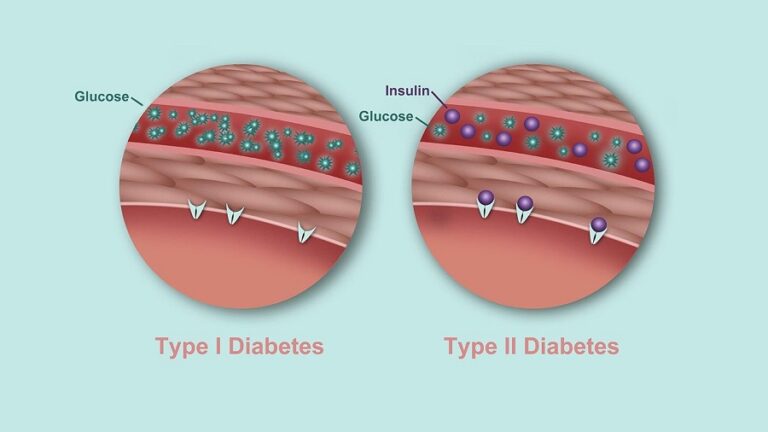
Insulin is one of the main human hormones in the human body. Its main function is to act as a key; As if it were opening gates, it allows the passage of glucose from the outside to the inside of the cell. Where it is then used as a source of energy. If there is not enough insulin available, or a person is unable to use it optimally, the disease diabetes appears.
Type 1 diabetes occurs when there is a lack of insulin synthesis and type 2 diabetes (95% of cases) is caused by poor diet. The body gets used to high levels and stops responding as it should. One of the main causes of diabetes is the regular consumption of large amounts of simple carbohydrates .
ABSTRACT
- The insulin index theory is a continuation of the glycemic index theory.
- In the insulin index, the calculated value refers to the ability to increase the levels of this hormone in the blood, not the amount of glucose that a food generates.
- A key difference in the insulin vs glycemic index charts is the effect of combining protein products with carbohydrates.
- Studies have shown that the presence of lactose with histidine causes a synergistic effect in increasing insulin.