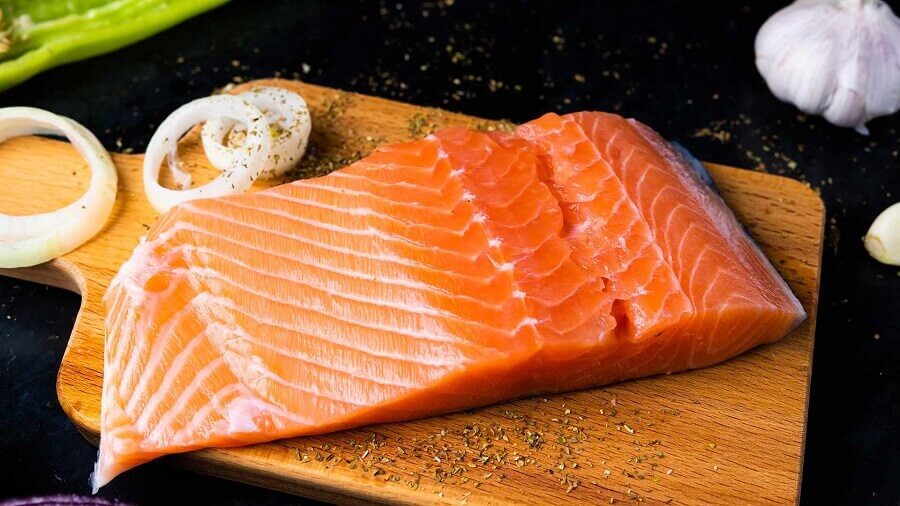
Salmon is one of the most popular fish. Both for its flavor and its nutritional properties.
However, the production of one type of salmon – farmed has questioned its health benefits in recent years.
This article details the nutritional properties of salmon meat and what are the differences between farm and wild salmon.
What is wild salmon?
Wild salmon is an all-encompassing term for salmon species that have not been raised on farms.
These are grouped as Atlantic Pacific salmon. As the name implies, the species of these salmon differ in their origin.
There are only one species in the Atlantic, and in the Pacific, there are five.
The easiest way to distinguish between one species and another is to observe the color of the meat. The Pacific salmon is pink, and that of the Atlantic is gray-brown.
What is farmed or farmed salmon?
Farmed salmon or farmed salmon is the type of salmon artificially raised on the ocean or on marine farms.
In this case, the Atlantic salmon species are raised for performance. So its original color is gray. The wild salmon we see in the supermarket is pink because it has been modified by including crustaceans and foods rich in carotenes and astaxanthin.
Farmed salmon is also usually genetically modified. And although today the trend is downward, antibiotics and hormones are still used in their production.
The farmed salmon farming method was created by the multinational pharmaceutical company Hoffman-LaRoche, and it even offers a color palette in its production.
Although astaxanthin is a harmless substance for health (3), it is a strategy used by multinationals to gain greater consumer appeal. Farm salmon is also usually genetically modified. Although the trend is downward, antibiotics are still used in their production.
Nutritional properties and benefits of salmon
It is generally known that salmon is meat with excellent nutritional properties.
In particular, salmon meat is high in protein and healthy fats.
The consumption of Omega-3 fatty acids present in salmon is related to a better cholesterol index and the prevention of chronic neurogenetic and cardiovascular diseases.
In addition, salmon is neutral meat that goes well gastronomically with many spices and accompaniments. The properties and benefits of salmon are:
- Improve skin health
According to a study carried out in Korea in 2005. EPA, one of the Omega-3 fatty acids, is a potential agent for preventing and treating skin aging. According to this study, consuming salmon could help improve skin health. (7)
- It can accelerate muscle recovery processes
One of the benefits of Omega-3 is to accelerate muscle recovery processes. The fatty acid n-3PFUA participates in the repair processes after intense physical activity. Positive results have been reported in reducing the recovery time of muscle fiber micro damages. (8)
- Regulate blood pressure
A high level of EPA and DHA fatty acids is directly related to improved blood pressure. One of the benefits of Omega-3 in the cardiovascular system is the reduction of inflammation and heart attacks, and it can act as an anticoagulant. (6)
- Can prevent neurodegenerative diseases
Regular consumption of DHA and EPA has a positive effect on improving cognitive functions. The benefits of Omega-3 from salmon have been proven to prevent psychological disorders such as Alzheimer’s. (6)
- Lower bad LDL cholesterol
Several studies affirm that one of the benefits of Omega-3s in salmon is to reduce bad LDL cholesterol. The fatty acids n -3 PUFA participate in the metabolism of cholesterol in the body. These compounds can reverse the transport of cholesterol and promote its elimination in the body. (10)
Differences between farm and wild
The first thing to think about is that it is better to eat any salmon than to eat none when it comes to salmon.
Including salmon in the diet at least twice a week is advised that any nutritionist will support. Provides protein, vitamin B12, cholesterol, iodine, selenium, and phosphorus
However, farmed salmon and wild salmon indeed have their nutritional differences.
First of all, both types of salmon are high in Omega-3 content. Contrary to what you might think, farmed salmon has more. This can be seen in the following table (2,6):
| Salmon species- production | Total fat (g) | Omega- 3 fatty acids (mg) | Cholesterol (mg) |
| Atlantic – Farm | 10.5 | 1,800 | 54 |
| King, Wild | 11.3 | 1,700 | 72 |
| Coho, Wild | 3.7 | 900 | 47 |
| Sockeye, Wild | 5.7 | 800 | 54 |
| Chum, Wild | 4.1 | 800 | 81 |
| Wild Rose | 4.5 | 700 | 55 |
However, the story does not end there. The main disadvantage of farmed salmon is that other fats are harmful to health.
These fats are derived from the diet they receive a fish meal. This flour is composed of other types of smaller fish. In this type of fat, chemicals that can be harmful to health accumulate.
This is one of the differences that leads to higher calorie content and lower amount of protein, and a higher probability of poisoning.
Furthermore, the boom in farmed salmon production is causing virtually irreversible changes in marine ecology. According to ecologists, with cultivated salmon farms, the trend is to eliminate the rest of the wild salmon species.
Farmed salmon How much does it affect the ecology?
Five kilos of wild fish are required to produce farmed salmon; the impact on the biodiversity of this fact is quite clear. Kilos and kilos of fish are used to obtain the delicious restaurant steaks.
To this must be added the effect of transport. In Chile, for example, 87% of salmon is exported to other parts of the world. Mainly the US and Japan (4). The cost of fuel generates an impact not only in the area where it is produced but also worldwide. Something similar occurs in the production of other species, such as pangasius.
Although, in most countries, projects must submit an environmental impact report, these factors are not taken into account by governments. Salmon farm projects are approved for purely economic benefits and not for real studies that accurately assess possible environmental impacts. Consuming this type of protein has its consequences for the environment.
ABSTRACT
- One of the properties of both types of salmon is their high content of Omega-3.
- The benefits of salmon are improving the cardiovascular system and the prevention of neurodegenerative diseases.
- Farmed salmon has a higher fat content and causes a severe ecological impact.