The body mass index is the most widely accepted and widely used ideal weight formula in healthcare facilities. This formula is also known as the Lorentz formula or BMI.
The Lorentz formula allows an approximate estimate of the ideal weight according to height; it is only necessary to resort to a table. It is the basis of the calculators and electronic devices on the market.
This article looks at how to calculate your ideal weight and what is the best formula that adapts to height with boards.
Lorentz’s ideal weight formula
The formula for calculating the ideal weight first emerged in medicine in the form of height minus one hundred (h – 100). A few later, it was corrected by Lorentz by adapting some parameters.
The formula of Lorentz’s ideal weight (2):
- [(height in cm – 100) – (height in cm – 150) / 4)] for men
- [(height in cm – 100) – (height in cm – 150) / 2)] for women.
For example, a 180 cm man should weigh 72.5 kg. Lorentz’s ideal weight formula was introduced in 1850. According to Lorentz, a woman who is 1.65 m tall should weigh 65 kg.
The body mass index (BMI) is a standard health assessment tool in most healthcare facilities.
Ideal weight table according to height
Below you can see a table of ideal weight according to height. The following table was made from the previous formulas:
| Height | Women | Men |
|---|---|---|
| 4′ 6″ (137 cm) | 63/77 lb (28.5/34.9 kg) | 63/77 lb (28.5/34.9 kg) |
| 4′ 7″ (140 cm) | 68/83 lb (30.8/37.6 kg) | 68/84 lb (30.8/38.1 kg) |
| 4′ 8″ (142 cm) | 72/88 lb (32.6/39.9 kg) | 74/90 lb (33.5/40.8 kg) |
| 4′ 9″ (145 cm) | 77/94 lb (34.9/42.6 kg) | 79/97 lb (35.8/43.9 kg) |
| 4′ 10″ (147 cm) | 81/99 lb (36.4/44.9 kg) | 85/103 lb (38.5/46.7 kg) |
| 4′ 11″ (150 cm) | 86/105 lb (39/47.6 kg) | 90/110 lb (40.8/49.9 kg) |
| 5′ 0″ (152 cm) | 90/110 lb (40.8/49.9 kg) | 95/117 lb (43.1/53 kg) |
| 5′ 1″ (155 cm) | 95/116 lb (43.1/52.6 kg) | 101/123 lb (45.8/55.8 kg) |
| 5′ 2″ (157 cm) | 99/121 lb (44.9/54.9 kg) | 106/130 lb (48.1/58.9 kg) |
| 5′ 3″ (160 cm) | 104/127 lb (47.2/57.6 kg) | 112/136 lb (50.8/61.6 kg) |
| 5′ 4″ (163 cm) | 108/132 lb (49/59.9 kg) | 117/143 lb (53/64.8 kg) |
| 5′ 5″ (165 cm) | 113/138 lb (51.2/62.6 kg) | 122/150 lb (55.3/68 kg) |
| 5′ 6″ (168 cm) | 117/143 lb (53/64.8 kg) | 128/156 lb (58/70.7 kg) |
| 5′ 7″ (170 cm) | 122/149 lb (55.3/67.6 kg) | 133/163 lb (60.3/73.9 kg) |
| 5′ 8″ (173 cm) | 126/154 lb (57.1/69.8 kg) | 139/169 lb (63/76.6 kg) |
| 5′ 9″ (175 cm) | 131/160 lb (59.4/72.6 kg) | 144/176 lb (65.3/79.8 kg) |
| 5′ 10″ (178 cm) | 135/165 lb (61.2/74.8 kg) | 149/183 lb (67.6/83 kg) |
| 5′ 11″ (180 cm) | 140/171 lb (63.5/77.5 kg) | 155/189 lb (70.3/85.7 kg) |
| 6′ 0″ (183 cm) | 144/176 lb (65.3/79.8 kg) | 160/196 lb (72.6/88.9 kg) |
| 6′ 1″ (185 cm) | 149/182 lb (67.6/82.5 kg) | 166/202 lb (75.3/91.6 kg) |
| 6′ 2″ (188 cm) | 153/187 lb (69.4/84.8 kg) | 171/209 lb (77.5/94.8 kg) |
| 6′ 3″ (191 cm) | 158/193 lb (71.6/87.5 kg) | 176/216 lb (79.8/98 kg) |
| 6′ 4″ (193 cm) | 162/198 lb (73.5/89.8 kg) | 182/222 lb (82.5/100.6 kg) |
| 6′ 5″ (195 cm) | 167/204 lb (75.7/92.5 kg) | 187/229 lb (84.8/103.8 kg) |
| 6′ 6″ (198 cm) | 171/209 lb (77.5/94.8 kg) | 193/235 lb (87.5/106.5 kg) |
| 6′ 7″ (201 cm) | 176/215 lb (79.8/97.5 kg) | 198/242 lb (89.8/109.7 kg) |
| 6′ 8″ (203 cm) | 180/220 lb (81.6/99.8 kg) | 203/249 lb (92/112.9 kg) |
| 6′ 9″ (205 cm) | 185/226 lb (83.9/102.5 kg) | 209/255 lb (94.8/115.6 kg) |
| 6′ 10″ (208 cm) | 189/231 lb (85.7/104.8 kg) | 214/262 lb (97/118.8 kg) |
| 6′ 11″ (210 cm) | 194/237 lb (88/107.5 kg) | 220/268 lb (99.8/121.5 kg) |
| 7′ 0″ (213 cm) | 198/242 lb (89.8/109.7 kg) | 225/275 lb (102/124.7 kg) |
Ideal Weight – New Formula
While the classic Lorentz formula is valid, many experts claim it is not ideal.
Although it has been used for decades as the gold standard for your health, it is not considered the most accurate formula. Many claims that BMI is outdated, inaccurate, and should not be used in medical and fitness settings.
According to a group of Stanford scientists, other formulas better approximate weight according to height. The procedure of the ideal weight, according to these specialists, is (3):
Ideal weight = 22 * height squared (IBW = 22 xh 2 )
According to obesity experts, this algorithm is a better ideal weight formula because it is better suited to the entire population.
In addition, experts note that while the new formula is better suited to ideal weight based on height, it is essential to know that it is not the best indicator of health.
Assessing a person’s health status by taking into account only the weight on the scale can oversimplify what it means to be healthy. There appears to be no correlation between mortality and average BMI values. (3)
For example, a change in body weight may be due to an increase or loss of water. Or you could be a good weight for your height but have diabetes, cholesterol, or excess fat in unhealthy parts of your body. Therefore, finding the ideal weight according to size should not be the only factor to consider if one wants to be healthy.
Ideal Weight – Excess Fat or Weight?
There are many cases where the body mass index of a person with a lot of fat could fall within the range according to height. In these situations, supplementing the formula to calculate the ideal weight with body fat percentage is essential to determine how healthy your body is.
Why isn’t the ideal weight formula the only thing that matters? Even if you have a perfect weight, an excess of fat in the body could be masking the risk of certain diseases, for example, those that affect your heart.
Fat is twice as light as muscle; even though you are at an ideal weight, you could have excess visceral fat in your body, associated with an increased risk of heart attacks.
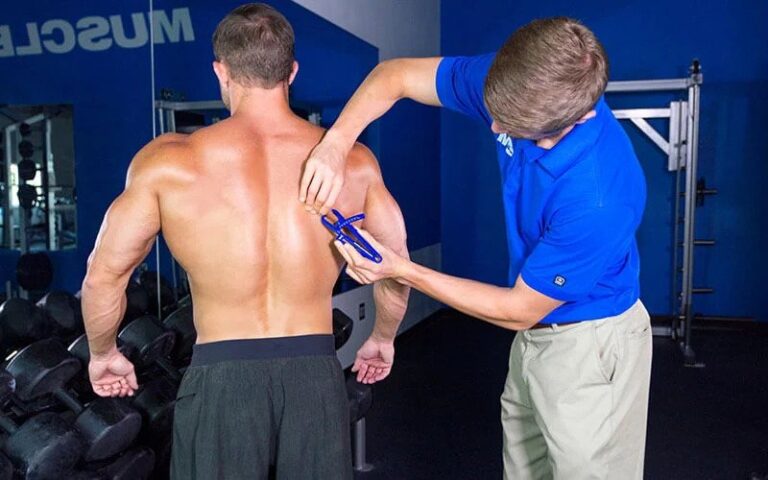
Ideal body fat percentage
While there is no formula for calculating your body fat percentage, several methods to achieve this. One of the most used is the caliper and tables. This method involves measuring the thickness of the subcutaneous fat folds in the abdomen. The values obtained in millimeters are compared with tables.
If you go to a nutrition professional, they will try to bring you to both values: the ideal weight and the ideal fat percentage.
The ideal body fat percentage ranges from 14-to 18% in men. While in women, the figure is 16-20%. Figures more significant than 25% are an indicator of an unhealthy state.
RELATED: Ideal Body Fat Percentage
ABSTRACT
The BMI is still the official indicator to determine whether a person is overweight. This calculation method works well when applied to people suffering from obesity.
Lorentz was the pioneer in applying the theory of the Body Mass Index, although today, science proposes other formulas of the ideal weight.
The BMI serves as an indicator of weight according to height, although it has several disadvantages: it does not consider the percentage of body fat. Therefore, taking into account only the BMI and its ideal weight formula according to height is not the most correct to know if one is healthy.